Cristoforo Colombo (Christopher Columbus) discovers America on behalf of Spain.
Giovanni Caboto (John Cabot) explores the Newfoundland coasts on behalf of Great Britain.
The Congrégation Notre-Dame, is founded in France by Pierre Fourier and Alix Le Clerc.
The first French colony on American soil is founded on Sainte-Croix Island, in Acadia, by Pierre Du Gua de Monts with Samuel de Champlain.
Samuel de Champlain founds Quebec, beginning French colonization in the Saint Lawrence River Valley.
The first Jesuits arrive in Acadia on a mission of evangelization.
The Récollets arrive in Quebec City for the purpose of converting the Amerindians to Christianity.
Marguerite Bourgeoys is born in Troyes (France).
The Jesuits arrive in Quebec City for the purpose of converting the Amerindians to Christianity.
Trois-Rivières is founded.
The Ursulines and the Augustinians, the first congregations of women in New France, arrive in Quebec City.
The first school for girls in North America is established in Quebec City by the Ursulines.
The Hôtel-Dieu de Québec is founded by the Augustinians.
The Société de Notre-Dame de Montréal pour la conversion des sauvages en Nouvelle-France is established in Paris.
Marguerite Bourgeoys hears God’s call during the procession in honour of Our Lady of the Rosary in Troyes (France).
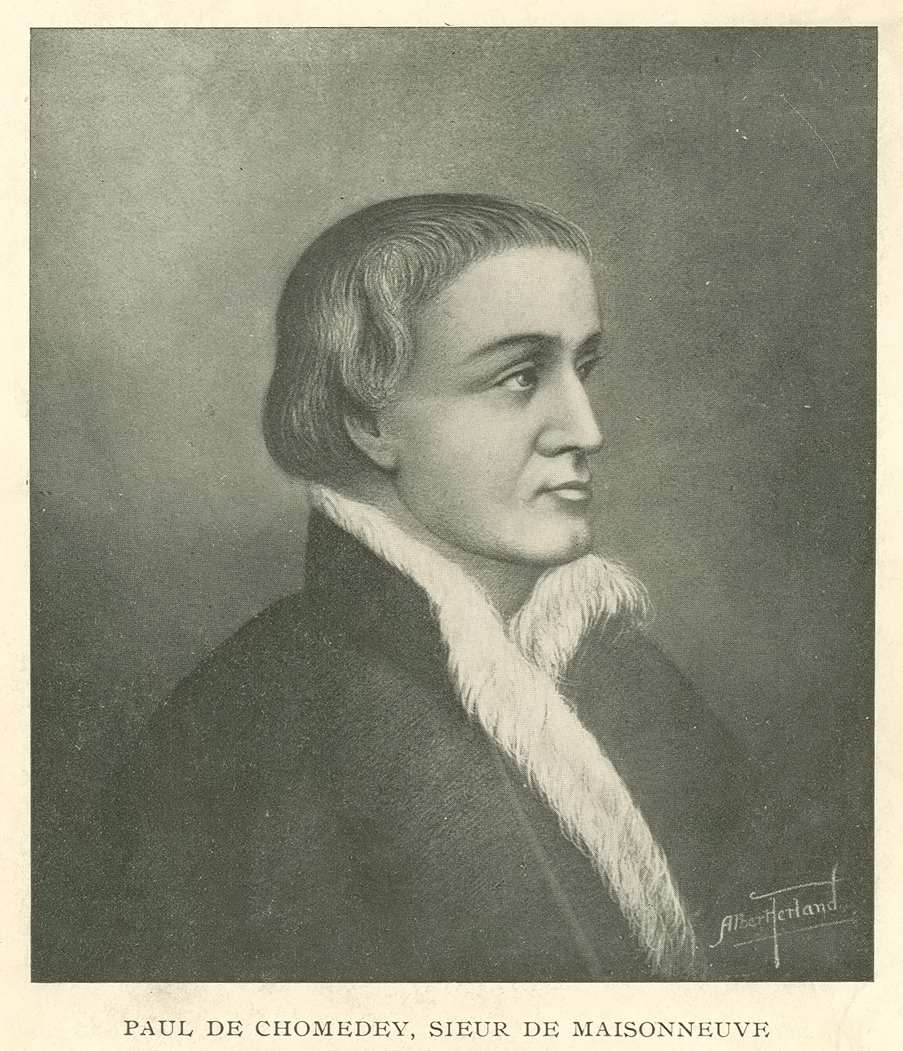
Ville-Marie (Montreal) is founded on behalf of the Société de Notre-Dame de Montréal by Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve with Jeanne Mance.
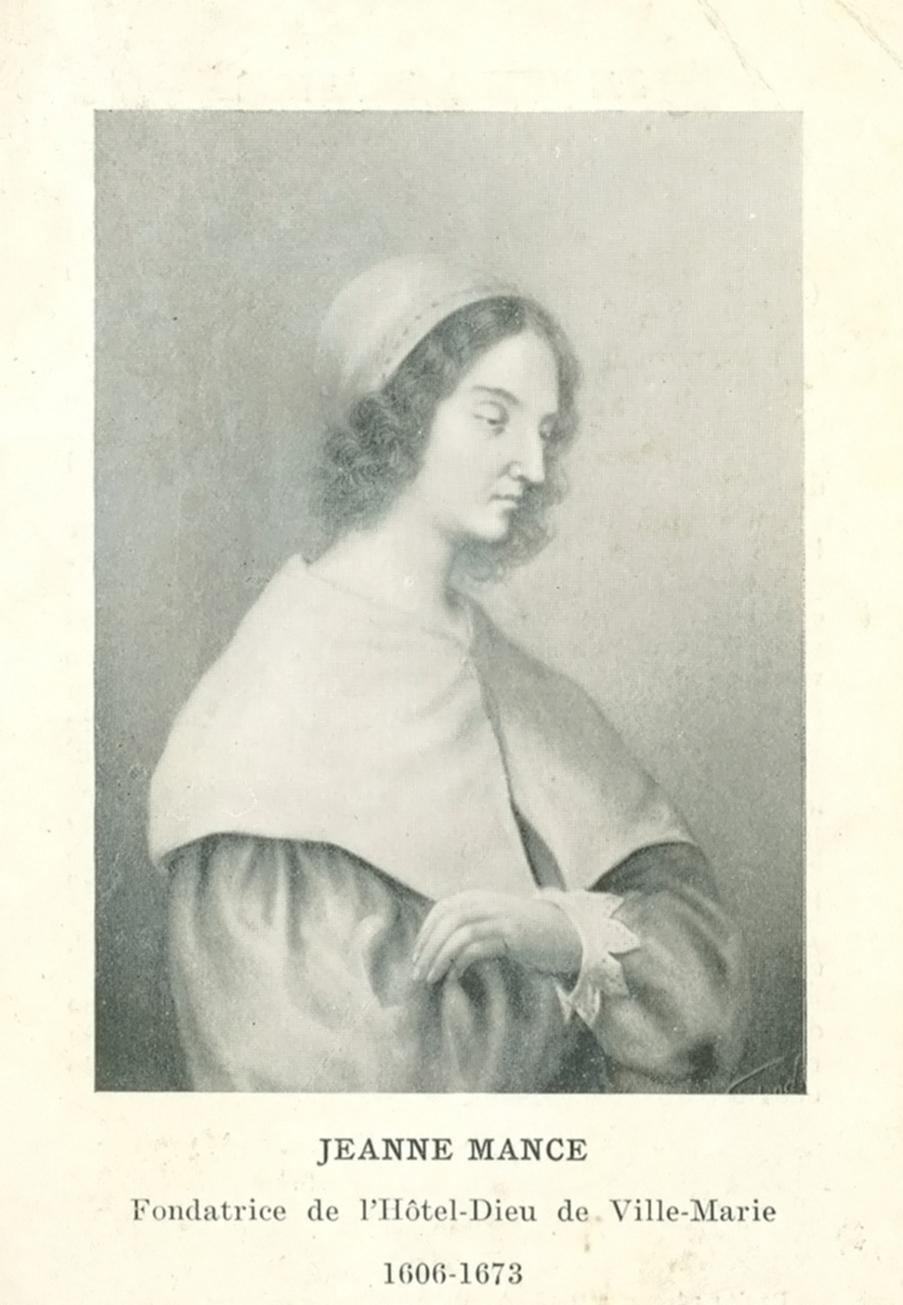
The Hôtel-Dieu de Montréal is founded by Jeanne Mance.
A wooden cross is erected on the Mont-Royal by Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve and his men, in thanksgiving for divine protection when the swollen waters of the Saint Lawrence River threatened the settlement on Christmas Day 1642.
A first peace treaty is negotiated between the French and the Iroquois.
The first baby girl, Barbe Meusnier, is born in Montreal.
Marguerite Bourgeoys, with a group of settlers, restores the wooden cross on the Mont-Royal which had been destroyed by the Iroquois.
Marguerite Bourgeoys meets Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve in Troyes (France).
Marguerite Bourgeoys arrives in Ville-Marie with la grande recrue (one-hundred new settlers).
A first attempt is made to build Notre-Dame-de-Bon-Secours Chapel.
The Sulpicians arrive in Ville-Marie (Montreal).
Marguerite Bourgeoys establishes the first school in Ville-Marie in a former stable. It was ceded to her by Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve on behalf of the “Messieurs les Associés pour la conversion des Sauvages de la Nouvelle-France” (Associates for the conversion of the savages in New France). Known as the stable-school and situated between Saint-Paul Street and the Saint Lawrence River, it is considered to be the first Mother House of the Congregation (1658-1673).
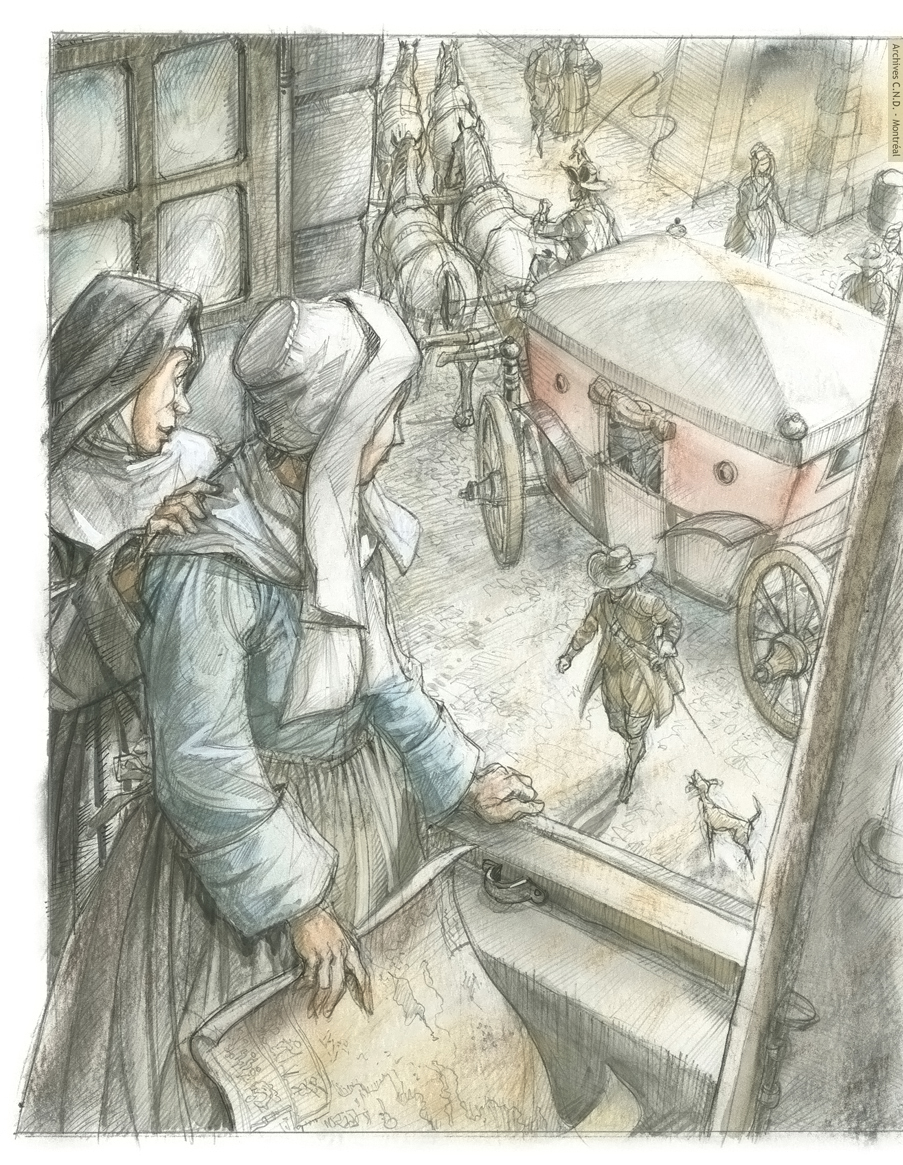
Marguerite Bourgeoys makes her first trip back to France with Jeanne Mance. Marguerite returns to Ville-Marie with her first companions, Edmée Châtel, Marie Raisin, Anne Hiou and Catherine Crolo. Jeanne Mance returns with the first Hospital Sisters of Saint-Joseph.
Bishop de Laval, first Bishop of Quebec, arrives in New France (1658 – 1688).
Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve cedes Pointe-Saint-Charles to Marguerite Bourgeoys.
The Société Notre-Dame de Montréal is disbanded and seigniorial rights to the Island of Montreal are transferred to the Séminaire Saint-Sulpice de Paris.
The first Filles du Roy (King’s Wards) arrive in New France (1663-1673).
Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve returns to France but remains governor of Montreal until 1669.
The citizens of Ville-Marie support Marguerite Bourgeoys in her attempt to obtain Letters Patent for the Congregation.
Bishop de Laval gives the Congregation permission to teach everywhere in his diocese which, at that time, comprises all of New France.
Marguerite Bourgeoys makes her second trip back to France (1670-1672).
The Hudson’s Bay Company is founded by Charles II, King of England.
The Institut des Filles séculières de la Congrégation de Notre-Dame obtains civil recognition in the form of Letters Patent granted by Louis XIV.
Second Mother House (1673–1683), known as the “large stone house”.
Bishop de Laval issues canonical approbation of the Institut des Filles séculières de la Congrégation de Notre-Dame.
Teaching of young Amerindians begins at the Mountain Mission, established in 1675 by the Sulpicians and the Sisters of the Congregation.
Notre-Dame-de-Bon-Secours Chapel is inaugurated after three years of construction.
Marguerite Bourgeoys makes her third trip back to France (1679-1680).
Marie-Thérèse Gannensagouas, first Sister of the Congregation of Amerindian origin, makes her private vows.
The Séminaire Saint-Sulpice is founded in Montreal.
The Mother House is destroyed by fire and Marguerite Sommillard and Geneviève du Rosoy perish in the blaze.
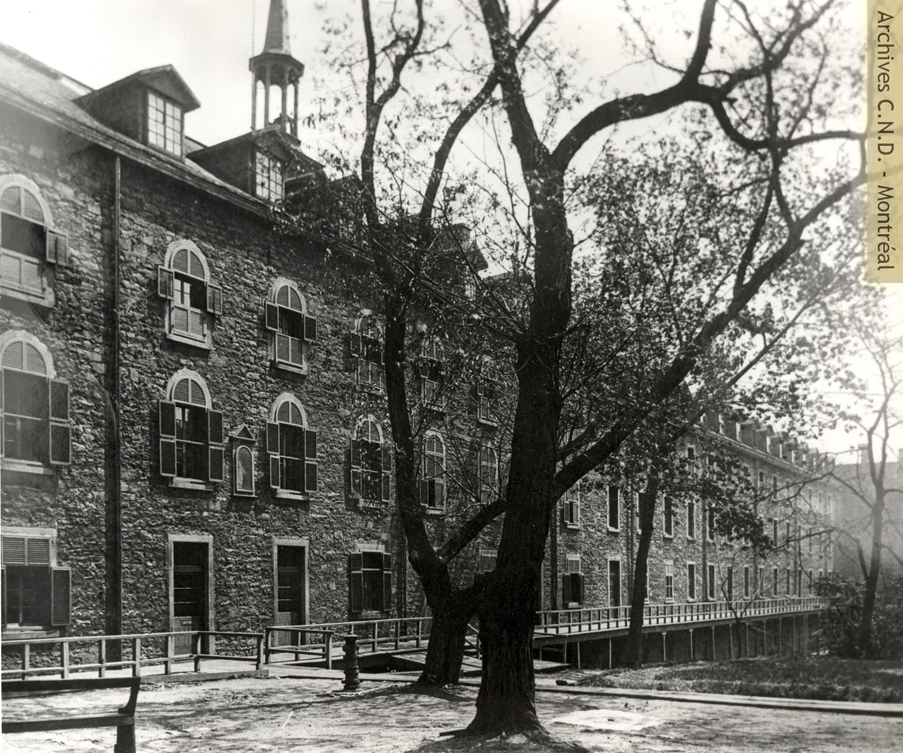
The third Mother House of the Congregation is established on Notre-Dame Street and is known as la maison sur le haut (1684–1844).
Marie Barbier (soeur de l’Assomption), first Sister of the Congregation born in Montreal, makes her private vows.
A wooden palisade is erected to protect the town of Montreal.
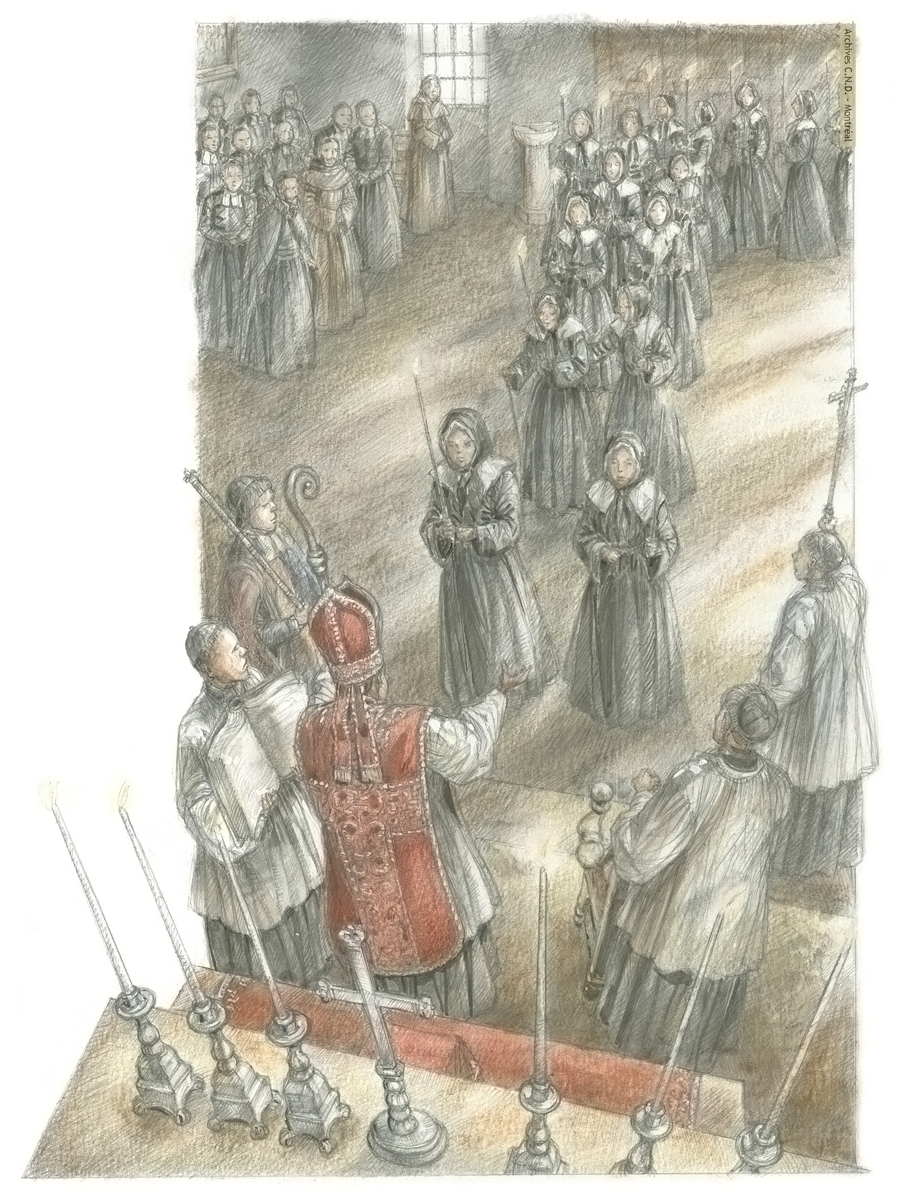
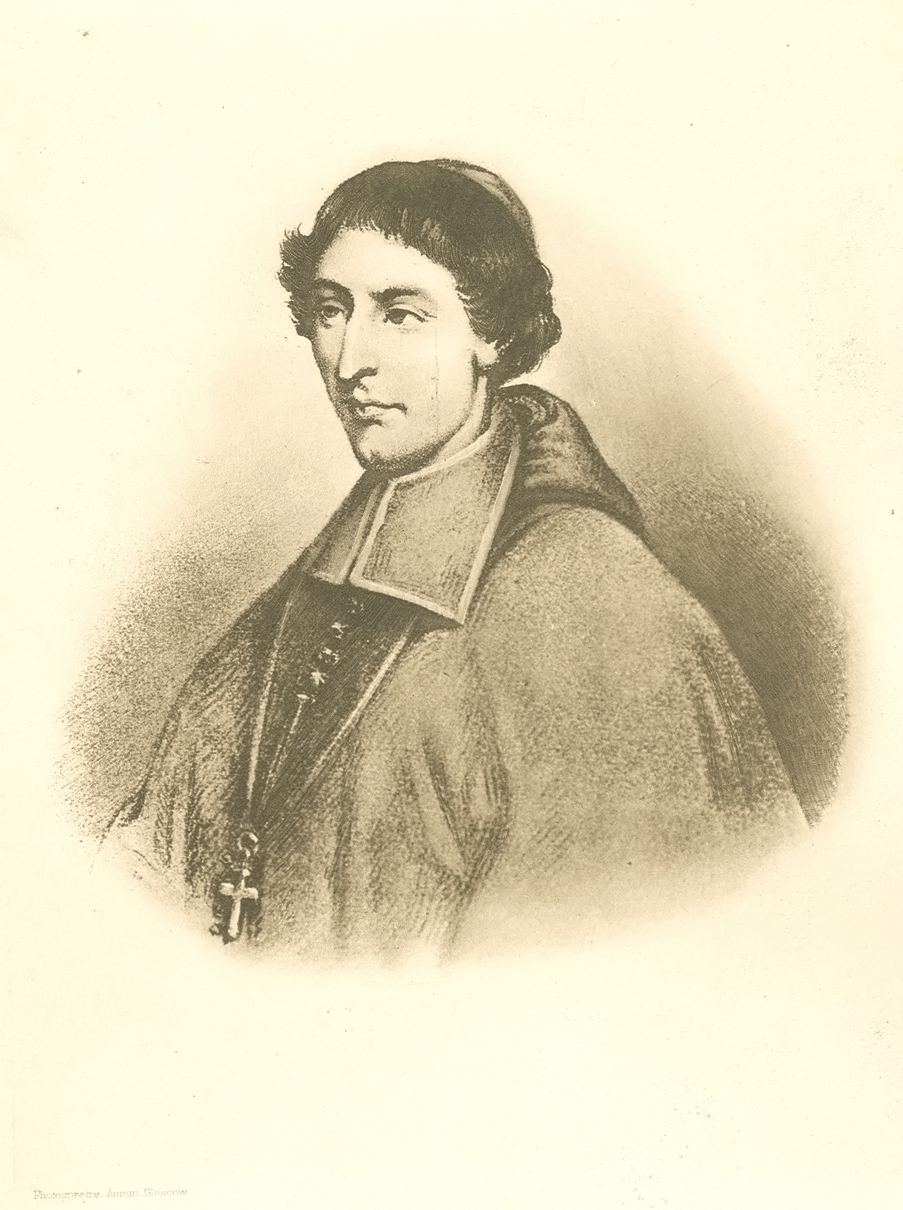
Bishop de Saint-Vallier begins his mandate as the second Bishop of Quebec (1688–1727).
Admiral Phips' fleet fails to capture Québec City.
Marie Barbier is elected second Superior of the Congregation.
Jeanne Le Ber goes into seclusion in an apartment in close proximity to the sanctuary in the chapel of the Sisters of the Congrégation de Notre-Dame, which she financed.
Lydia Longley (soeur Sainte-Madeleine), first English-speaking Sister of the Congregation from the colonies that would later become the United States, makes her private vows.
Marguerite Bourgeoys writes her memoirs.
The Sisters accept the rules written by Bishop de Saint-Vallier and the first religious professions take place in Ville-Marie (Montreal) and in Quebec.
Marguerite Bourgeoys dies in Ville-Marie.
The Great Peace Treaty of Montreal was signed by Sieur de Callière of France and representatives of thirty-nine Amerindian nations.
The War of Spanish Succession begins (1702-1714).
The invading British fleet under the command of Admiral Walker is shipwrecked in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.
The Treaty of Utrecht is signed bringing to an end the War of Spanish Succession. France cedes to Great Britain her claims to Hudson Bay, Newfoundland, and Acadia.
The construction of the fortress of Louisbourg (Cape Breton Island) begins.
A school of the Congregation is established in Louisbourg (Cape Breton Island, in what is known today as Nova Scotia).
Bishop de Saint-Vallier dies.
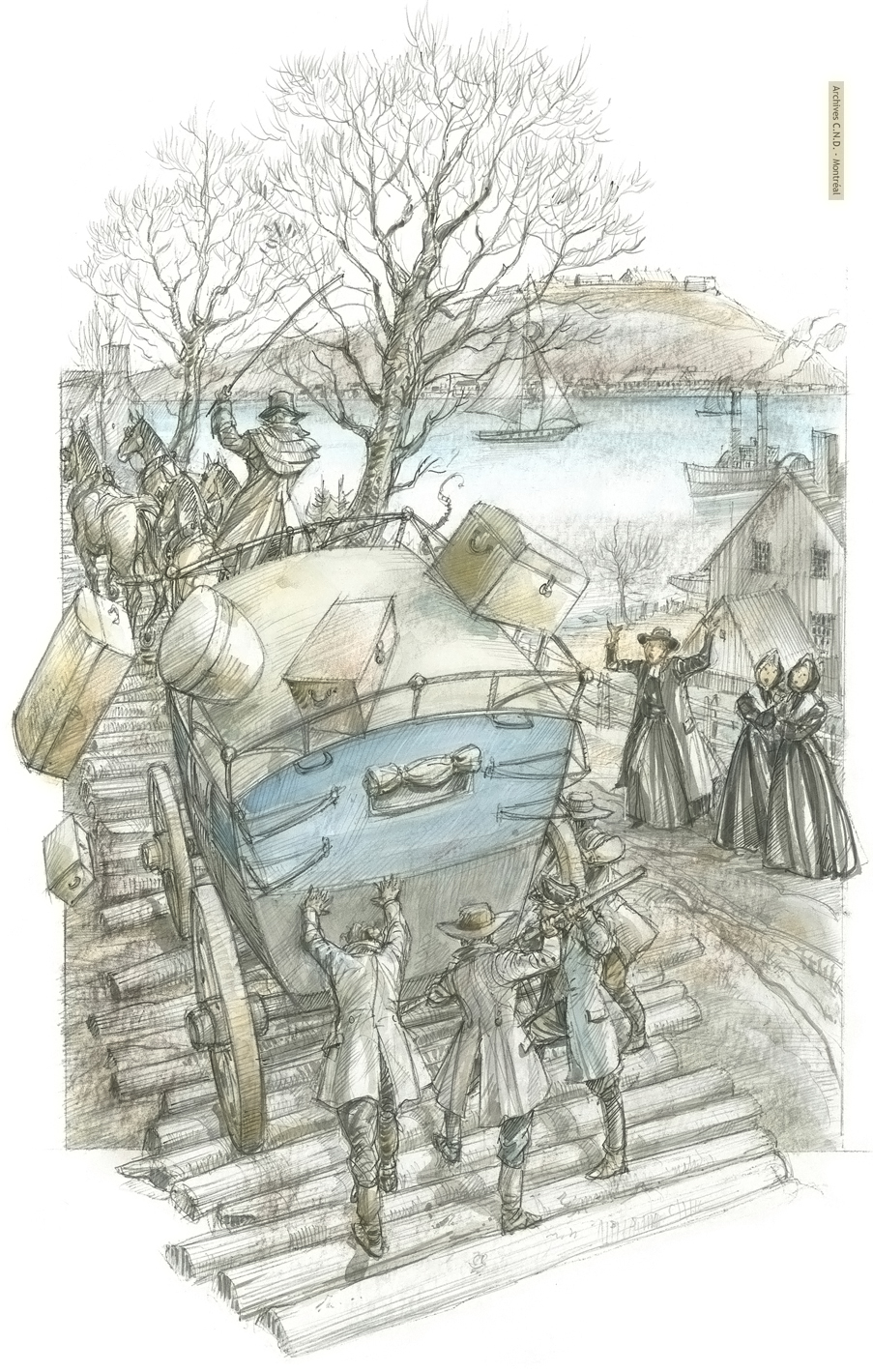
First siege of Louisbourg: The Sisters, students and their families are deported to France.
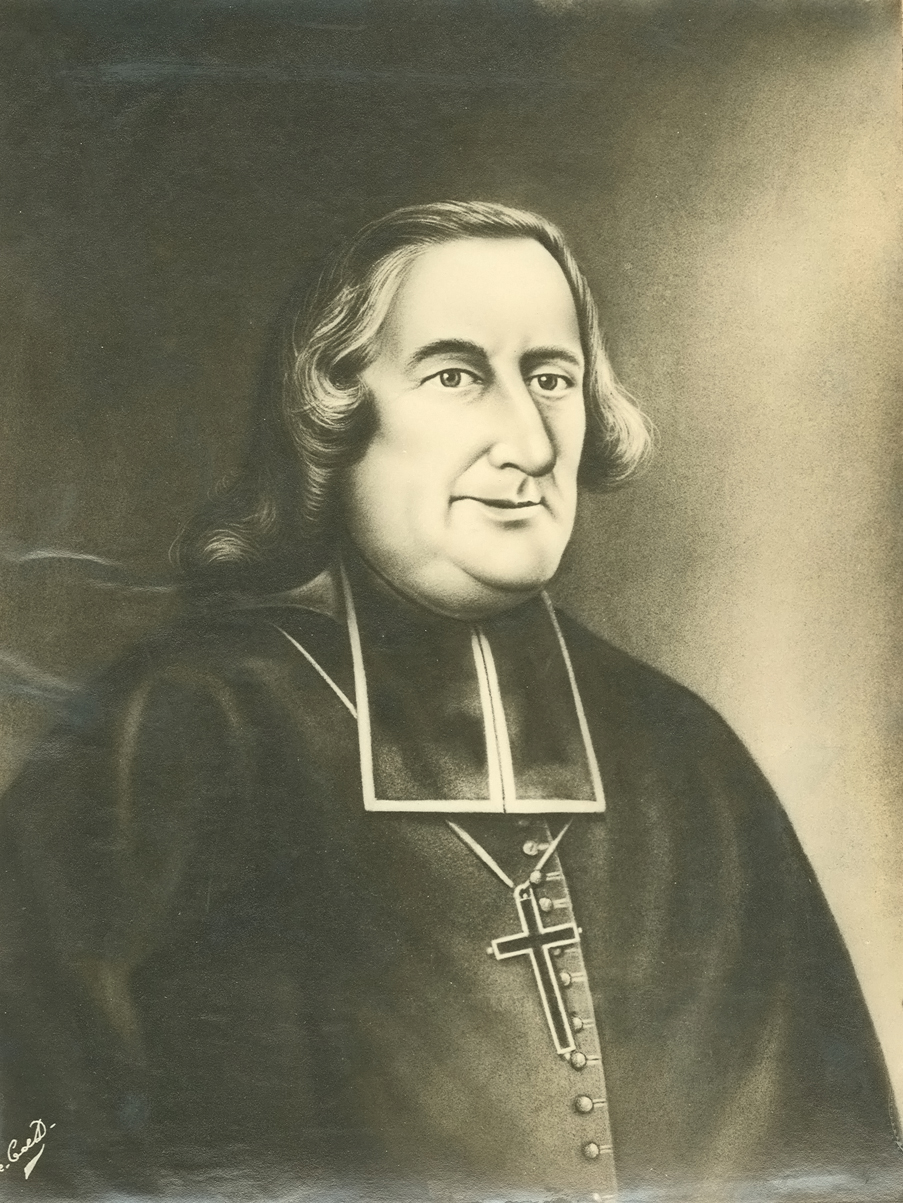
Bishop de Pontbriant restricts membership in the Congregation to eighty.
Louisbourg is returned to French control.
Surviving Sisters of the Congregation return to Louisbourg, where they find their houses destroyed.
Notre-Dame-de-Bon-Secours Chapel is destroyed by fire.
The Seven Years War begins (1754–1760).
The British deport over 8,000 Acadians to France and throughout the Americas.
Second siege of Louisbourg: The Sisters, students and their families are deported to France.
Quebec is captured by the British following the Battle of the Plaines d’Abraham.
The British take possession of Montreal.
The Treaty of Paris is signed ending the Seven Years War. France cedes most of its North American possessions to Great Britain.
The British Royal Proclamation of 1763 renames New France the “Province of Quebec.”
Seigniorial rights to the Island of Montreal are ceded by the Séminaire Saint-Sulpice de Paris to the Séminaire Saint-Sulpice de Montréal.
The first newspaper, La Gazette de Québec, is published in Quebec City.
The Mother House of the Congregation is destroyed by fire. It is rebuilt in 1769 and continues to be used until 1844.
The Congregation purchases the last piece of property on Île Saint-Paul (today Nun’s Island) and becomes its sole owner.
Saint John's Island (renamed Prince Edward Island in 1799) was granted colonial status independent of Nova Scotia.
Notre-Dame-de-Bon-Secours Chapel is rebuilt (1771-1773).
The British Parliament passes the Quebec Act that allowed Quebec to maintain the French language, the French Civil Code as its judicial system and sanctioned the freedom of religious choice, allowing the Roman Catholic Church to remain.
The War of Independence begins (1775–1783).
Montreal surrenders to the Americans under the command of General Richard Montgomery. The Americans unsuccessfully attempt to capture Quebec.
The American Declaration of Independence is signed.
The North West Company of Montreal is officially created.
The Treaty of Paris is signed, formally ending the American Revolutionary War and granting independence to the United States. (Please note: this “treaty of Paris” is not to be mistaken for the 1763 Treaty of the same name).
Britain splits the colony of Nova Scotia into three separate colonies: New Brunswick, Cape Breton Island, and present-day peninsular Nova Scotia.
The Constitutional Act splits the province of Quebec into Upper Canada (Ontario) and Lower Canada (Quebec). It grants all landowners, regardless of gender, voting rights to elect representatives to the Legislative Assembly.
Lower Canada (Quebec) passes the first Schools Act, known as Royal Institution, in order to create the establishment of an entirely state-subsidized system.
The War of 1812 begins between the United States and Canada (1812–1815).
The Diocese of Montreal is established as autonomous with respect to the one in Quebec City.
The second Schools Act, known as The Parish Schools Act, which allows the creation of parish schools, is passed.
The third Schools Act, known as The Trustees Schools Act, which allows the creation of schools subsidized by the Legislative Assembly and managed by trustees elected by resident landholders, is passed.
The Charter of incorporation for the city of Montreal is established and the first elections are held. Jacques Viger is elected first mayor of Montreal.
Slavery is abolished in Lower Canada.
The Diocese of Montreal is canonically erected by Pope Gregory XVI.
Rebellions by the patriots in Lower Canada and by the reformists in Upper Canada take place (1837–1838).
The Act of Union combines Lower Canada and Upper Canada.
The first English-language school of the Congregation is founded in Kingston (in what is known today as Ontario).
The fourth Schools Act, which creates the basis for a denominational schools system, is passed.
Bishop Bourget lifts the membership restriction.
The fourth Mother House of the Congregation is established on Saint-Jean-Baptiste Street (1844-1880).
The fifth Schools Act, which establishes self-governing school boards, is passed. In Montreal and Quebec, Catholic and Protestant school boards are created.
The Rebellion Losses Bill is enacted to compensate Lower Canadians who lost property during the Rebellions of 1837–1838.
The municipal right to vote of women landowners is withdrawn.
The seigniorial system is abolished.
Ottawa is designated as the capital of Canada.
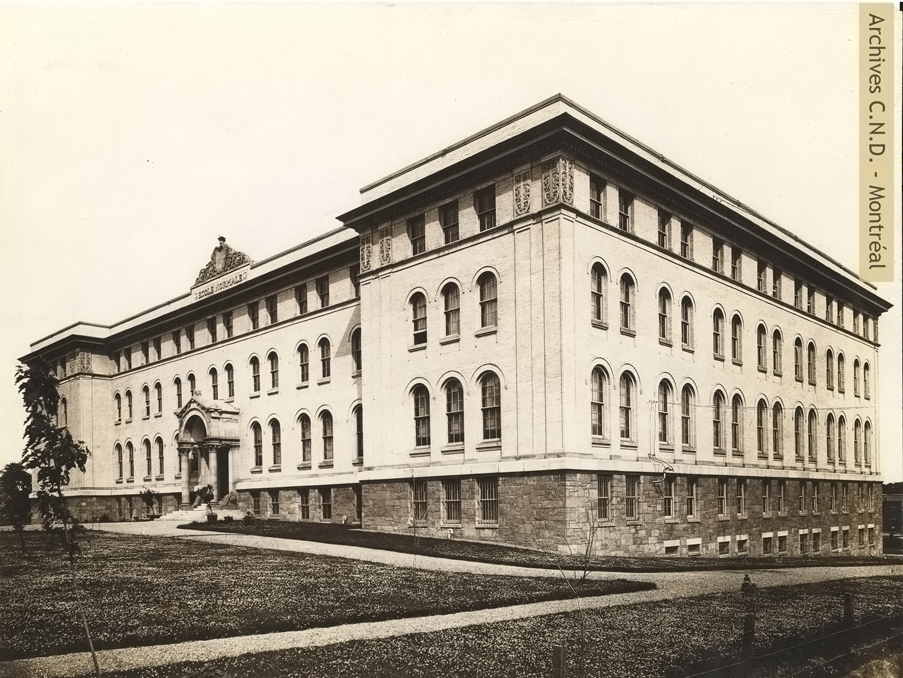
The first normal schools, or teacher training institutions, are established: two French-language and Catholic, the École normale Jacques-Cartier de Montréal and the École normale de Laval in Quebec, for girls; one English-language and Protestant, the MacDonald Normal School, affiliated to McGill University, which is mixed.
The Council of Public Instruction is established to administer Quebec’s public school system.
The first mission of the Congregation in the United States (Bourbonnais, Illinois) is established.
The British North America Act establishes the Dominion of Canada formed by the confederation of the provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec and Ontario.
Quebec’s first Ministry of Public Instruction is established.
Manitoba, the Northwest Territories, and Rupert’s Land join Confederation.
The Compulsory School Attendance Act is passed in Ontario.
British Columbia joins Confederation.
Prince Edward Island joins Confederation.
The Indian Act is passed by the Federal Government.
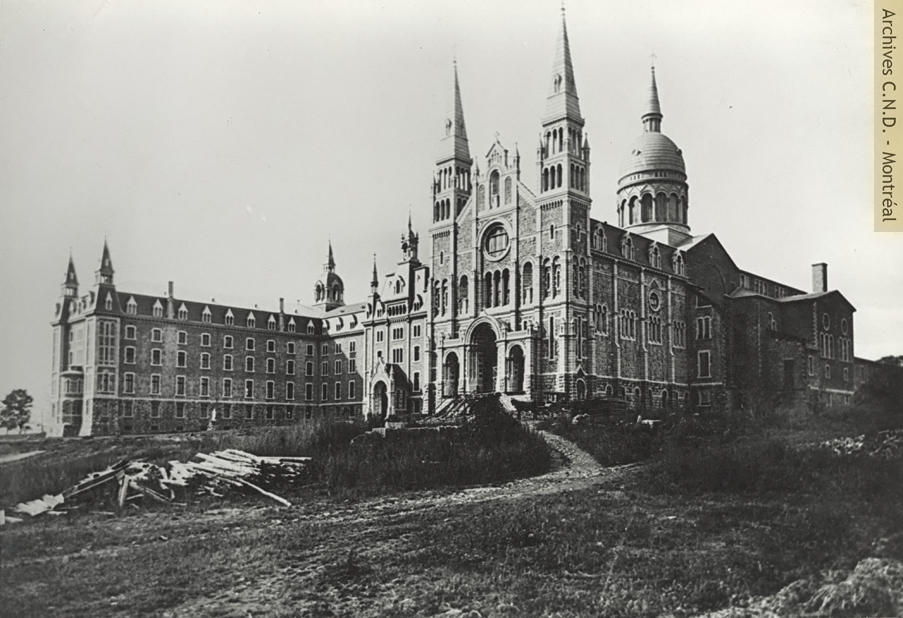
The fifth Mother House of the Congregation, known as the “Mother House on the Mountain” is established (1880-1893).
Unmarried women landowners obtain the right to vote in municipal elections in Ontario.
Following the Métis rebellion in western Canada, Louis Riel is tried and hung in Regina.
The first undergraduate degrees from the Faculty of Arts and from the Normal School are granted to women by Montreal’s English-language McGill University.
Women who have attained their majority and widowed landowners obtain the right to vote in federal elections.
Widows and single women who have attained majority obtain the right to vote in municipal elections in Quebec.
The Mother House is destroyed by fire. The Sisters return to the Mother House on Saint-Jean-Baptiste Street (1893-1908).
The Congrégation de Notre-Dame participates in the Pan-American Exposition in Chicago.
The first undergraduate diplomas are granted by Mount Saint Bernard College, the first post-secondary institution for women in North America. The college was established by the Congregation in Antigonish, Nova Scotia in 1883.
The women’s branch of the École normale Jacques-Cartier de Montréal opens under the jurisdiction of the Congregation.
The Paris World’s Fair is held.
The Federal Government splits the Northwest Territories to create the provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan.
The Congregation’s first commercial class opens in Pointe Saint-Charles.
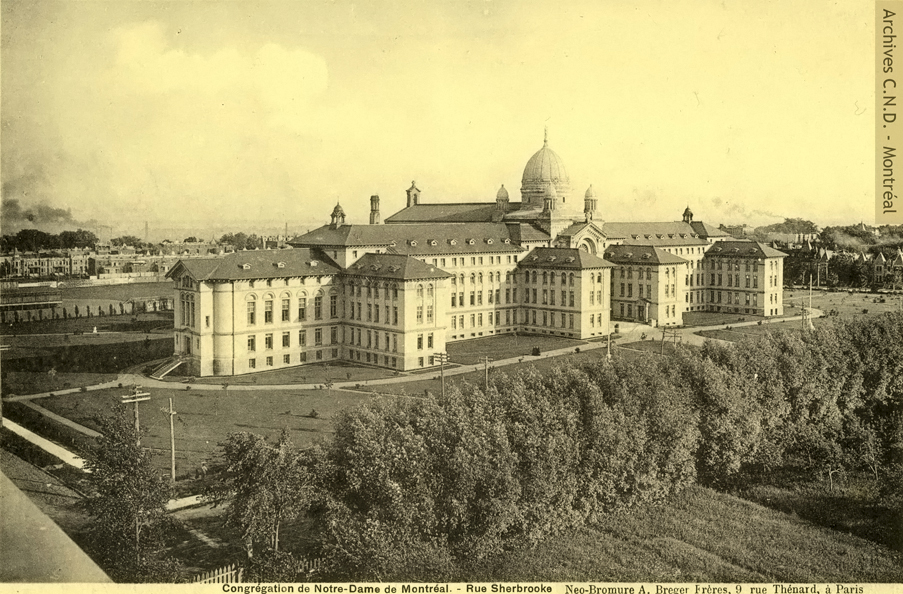
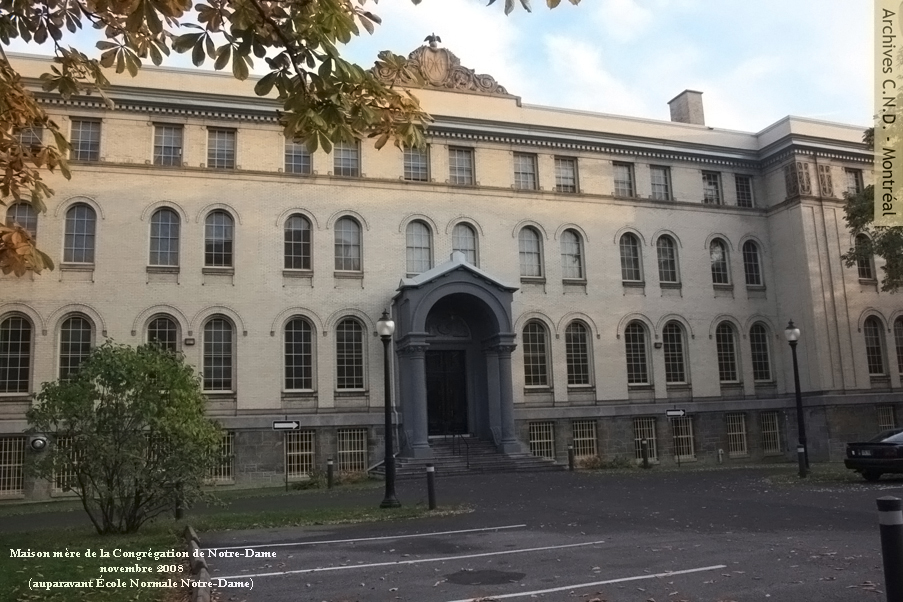
The Congregation’s sixth Mother House is established at 3040 Sherbrooke Street (1908-1985).
The first collège classique for women in Quebec, the École d’enseignement supérieur pour jeunes filles, opens in the Mother House under the jurisdiction of the Congregation. In 1926 it becomes Collège Marguerite-Bourgeoys.
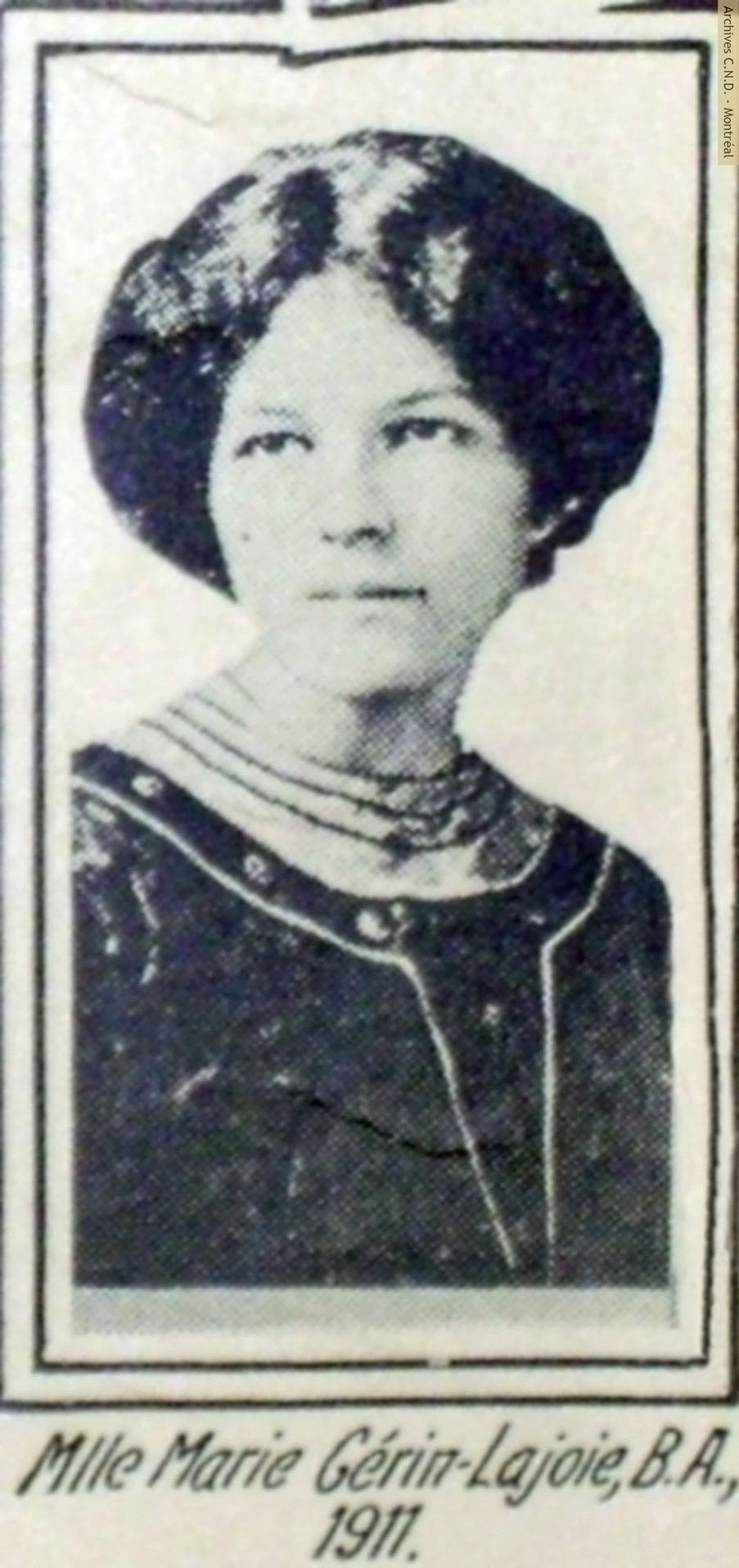
Marie Gérin-Lajoie, first graduate of the École d’enseignement supérieur pour jeunes filles, obtains first place at the Baccalauareat exams.
Marie Gérin-Lajoie becomes the first woman to receive a BA degree from a French University.
World War I begins (1914–1918).
Women with family ties to a person in the military obtain the right to vote in federal elections. Women obtain the right to vote in provincial elections in Ontario and British Columbia.
All women obtain the right to vote in federal elections.
The Lettres et sciences programme, a stepping stone to university education, is established in many schools of the Congregation in Quebec.
A new programme of studies leading to a Baccalaureate in Household Economy is offered by the Congregation at Mount Saint Bernard College in Antigonish, Nova Scotia.
The first mission of the Congregation in Japan (Fukushima) is established.
Married women whose marriage does not have a community property clause, who are landowners or who hold a lease in Montreal obtain the right to vote to municipal elections.
World War II begins (1939–1945).
All women obtain the right to vote in Quebec (Provincial level).
The war in the Pacific (1941-1945) begins: Canadian Sisters living in Japan are kept as prisoners.
Women in Quebec who pay the poll tax obtain the right to vote in municipal elections.
Newfoundland joins Confederation.
Marguerite Bourgeoys is beatified by Pope Pius XII.
Aboriginal peoples obtain the right to vote in federal elections.
The Royal Commission on Education, known as the Parent Commission, whose mandate is to completely reform the school system in Quebec, is established.
The first mission of the Congregation in Latin America (Tegucigalpa, Honduras) is established.
The reports stemming from the Royal Commission on Education are issued (1963-1966).
The first mission of the Congregation in Guatemala is established.
The Ministry of Education of Quebec is established.
The first mission of the Congregation in Chile (1965-1973) is established.
The second Ecumenical Council of the Catholic Church held at the Vatican, known as Vatican II, ends. It focused on opening the Catholic Church to the modern world.
Saint-Gabriel Museum in Pointe Saint-Charles de Montréal is inaugurated
The Montreal World’s Fair is held.
C.E.G.E.Ps (Collège d'enseignement général et professionnel) are created in Quebec.
The normal schools and domestic science schools are closed.
Comprehensive schools are established.
Aboriginal peoples obtain the right to vote in provincial elections.
The first mission of the Congregation in Africa (Cameroon) is established.
The Quebec Charter of Rights and Freedoms is adopted.
The CND Associate Relationship, a group of lay persons committed to living the mission and charism of Marguerite Bourgeoys, is founded.
The Sisters of the Congrégation de Notre-Dame settle in Troyes, France.
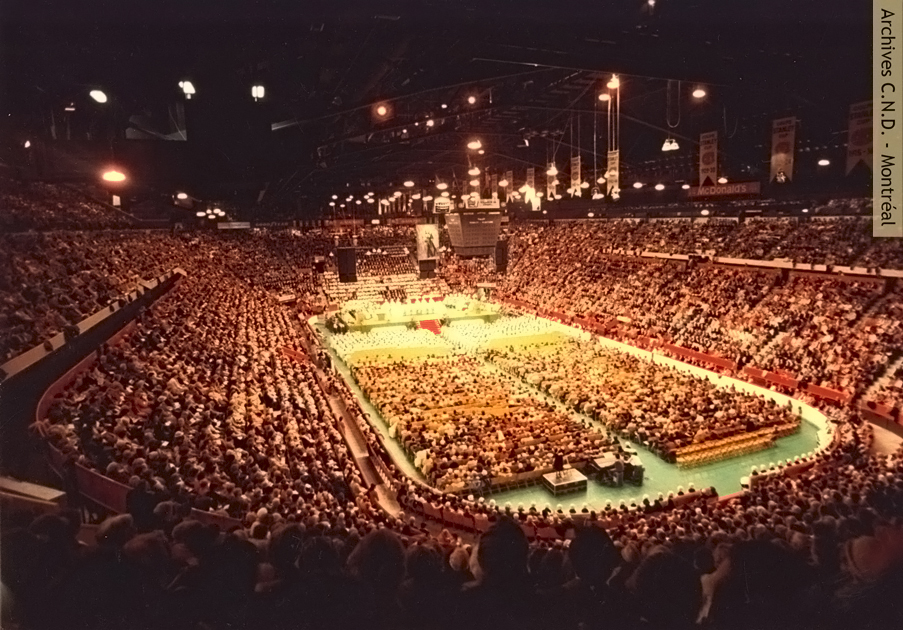
Marguerite Bourgeoys is canonized by Pope John Paul II. She is the first saint of the Canadian Church.
The seventh Mother House of the Congregation is established on Westmount Avenue (1985-2005).
The first mission of the Congregation in El Salvador is established.
School boards according to language replace denominational ones.
Marguerite-Bourgeoys Museum opens in the historic district of Old Montreal.
The eighth Mother House of the Congregation is established at 2330 Sherbrooke Street West.